
Table of Contents
1. Introduction – Why Focus Improvement Matters in a Distracted World
Focus improvement has become one of the most essential mental skills in today’s fast paced and distraction filled world. Phones, notifications, social media, constant messages, and information overload pull attention in multiple directions every minute. The brain rarely gets uninterrupted time to think deeply or work calmly. Over time, this constant stimulation trains the mind to expect interruption. As a result, many people struggle to concentrate, stay present, or complete tasks without checking something else. This weakens attention strength and reduces mental clarity.
Focus improvement matters because a scattered mind creates ongoing stress and dissatisfaction. When attention keeps jumping, tasks take longer than necessary and mental effort increases. Mistakes become more common because the mind is never fully engaged. Even after working all day, people often feel mentally exhausted yet unfulfilled. This mental overload drains motivation and creates a sense of inner pressure where the mind feels busy but unproductive.
Focus improvement is closely linked to mental wellness and emotional balance. A focused mind feels calmer because it is not constantly reacting to external triggers. When attention is stable, emotions settle more easily and anxiety reduces. Decision making improves because thoughts become clearer and more organized. This sense of mental control builds confidence and emotional stability. Over time, a focused mind supports long term mental health.
Focus improvement is not about forcing the brain to concentrate harder through pressure or strict discipline. Forcing focus often creates resistance, frustration, and burnout. Instead, focus improves when we understand how modern habits weaken attention. Endless scrolling, multitasking, and constant stimulation train the brain to avoid stillness and depth. Recognizing this helps people work with the brain rather than against it. Awareness becomes the starting point of real change.
Focus improvement is possible for anyone because focus is a trainable skill, not a fixed trait. The brain adapts to how it is used daily, whether that use is shallow or deep. With supportive routines, healthy boundaries, and consistent attention training, focus can be rebuilt naturally. Small daily changes create powerful long term results. Gradually, mental clarity, patience, and concentration return. This article explores how focus works, why it weakens, and how it can be strengthened sustainably.
2. Understanding Focus and Attention – How the Brain Concentrates
Focus improvement begins with understanding how attention works inside the brain. Focus is the ability to direct mental energy toward one task, thought, or experience while filtering out distractions. Attention is limited and sensitive, not endless. When it is constantly used without rest, it weakens quickly. The brain needs pauses to recover and reset. Without recovery, focus becomes fragile and inconsistent.
Focus improvement becomes difficult when the brain is overstimulated throughout the day. The brain is naturally designed to notice new information, which once helped humans stay safe. In modern life, this same system is triggered by notifications, messages, and fast moving content. Each interruption pulls attention away from the present task. Over time, the brain learns to seek novelty instead of stability. This makes sustained focus feel uncomfortable.
Focus improvement is strongly affected by multitasking, even though it feels productive. The brain cannot truly focus on multiple things at the same time. Instead, it switches rapidly between tasks, losing efficiency with each switch. This constant switching increases mental fatigue and reduces accuracy. Over time, it weakens attention span and memory. Deep thinking becomes harder because the brain is trained for speed, not depth.
Focus improvement depends on strengthening neural pathways related to sustained attention. Neuroscience shows that the brain changes based on repeated behavior. Each time attention stays on one task without distraction, focus related pathways grow stronger. Gradually, the brain becomes more comfortable with stillness and depth. Distractions lose their grip, and concentration feels more natural. This process requires patience but delivers lasting results.
Focus improvement becomes easier when self blame is removed from the process. Difficulty concentrating is not a sign of laziness, weakness, or low intelligence. It is a learned response to modern environments and habits. Once this is understood, people stop fighting themselves mentally. Focus training becomes supportive rather than stressful. With awareness, consistency, and compassion, attention can be rebuilt, stabilized, and deepened naturally.
3. Common Reasons for Poor Focus and Scattered Attention
Focus improvement becomes difficult when everyday habits silently weaken attention over time. One of the biggest causes is digital overload. Constant screen exposure trains the brain to expect quick rewards and frequent stimulation. Notifications, short videos, and rapid scrolling fragment attention into small pieces. As a result, the mind loses its ability to stay with tasks that require patience, effort, or deep thinking. Gradually, sustained focus starts to feel uncomfortable.
Focus improvement is also strongly affected by mental and emotional stress. When the brain is under constant pressure, attention naturally shifts toward worries, fears, and unfinished thoughts. Even when the body is physically resting, the mind may remain active and noisy. This inner mental chatter consumes attention energy. Deep focus becomes difficult because the brain is busy trying to solve emotional problems rather than concentrating on the present task.
Focus improvement weakens significantly when sleep quality is poor. Sleep is essential for restoring attention, memory, and mental clarity. When sleep is irregular or shallow, the brain struggles to process information efficiently. Reaction time slows, concentration drops, and mental fatigue increases. Over time, lack of proper sleep reduces the brain’s ability to control attention and resist distractions.
Focus improvement is further damaged by unstructured routines and lack of daily rhythm. When the day has no clear structure, the brain wastes energy deciding what to do next. This constant decision making leads to decision fatigue. Mental energy gets drained before meaningful work even begins. Without routine, attention becomes scattered and inconsistent throughout the day.
Focus improvement becomes possible only when these root causes are recognized and addressed. Focus does not return through willpower alone. It improves when lifestyle conditions support attention naturally. Reducing digital overload, managing stress, improving sleep, and creating structure all work together. Awareness of these factors creates the foundation for rebuilding strong, stable focus.

4. Daily Habits That Strengthen Focus and Attention
Focus improvement becomes stronger when daily habits support the brain instead of overwhelming it. The brain functions best when it knows what to expect each day. Fixed wake up times, planned work hours, and regular breaks reduce mental confusion and anxiety. When routines are predictable, the brain does not waste energy adjusting constantly. This mental stability creates the right conditions for deeper concentration and longer attention spans.
Focus improvement depends heavily on how digital habits are managed. Constant phone checking, message alerts, and social media scrolling interrupt attention again and again. Each interruption forces the brain to restart focus, which is mentally exhausting. Over time, this trains the brain to expect distraction instead of depth. Setting clear boundaries such as limited notifications, fixed screen times, and phone free work sessions allows attention to remain steady and uninterrupted.
Focus improvement increases when the mind is trained to stay present instead of wandering automatically. Practices like mindfulness, slow breathing, or single task attention exercises help build awareness. These practices teach the brain to notice distractions without immediately reacting to them. With regular practice, the urge to switch tasks weakens and the mind becomes calmer. Presence slowly replaces restlessness, making focus feel more natural.
Focus improvement is strongly influenced by physical habits that support brain health. Quality sleep restores attention control and improves mental sharpness. Regular movement increases blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients needed for clear thinking. Even light exercise helps reduce mental fog and improve alertness. Proper hydration and balanced meals also prevent energy crashes that weaken focus during the day.
Focus improvement grows when rest is treated as an essential part of productivity. Continuous work without breaks drains attention quickly and leads to mental fatigue. Short, intentional breaks give the brain time to reset and recover. Stepping away from screens, stretching, or simply sitting quietly helps restore mental energy. When work and rest are balanced, focus becomes sustainable instead of exhausting.
5. Focus Improvement Habits: 10 Daily Practices for Deep Focus
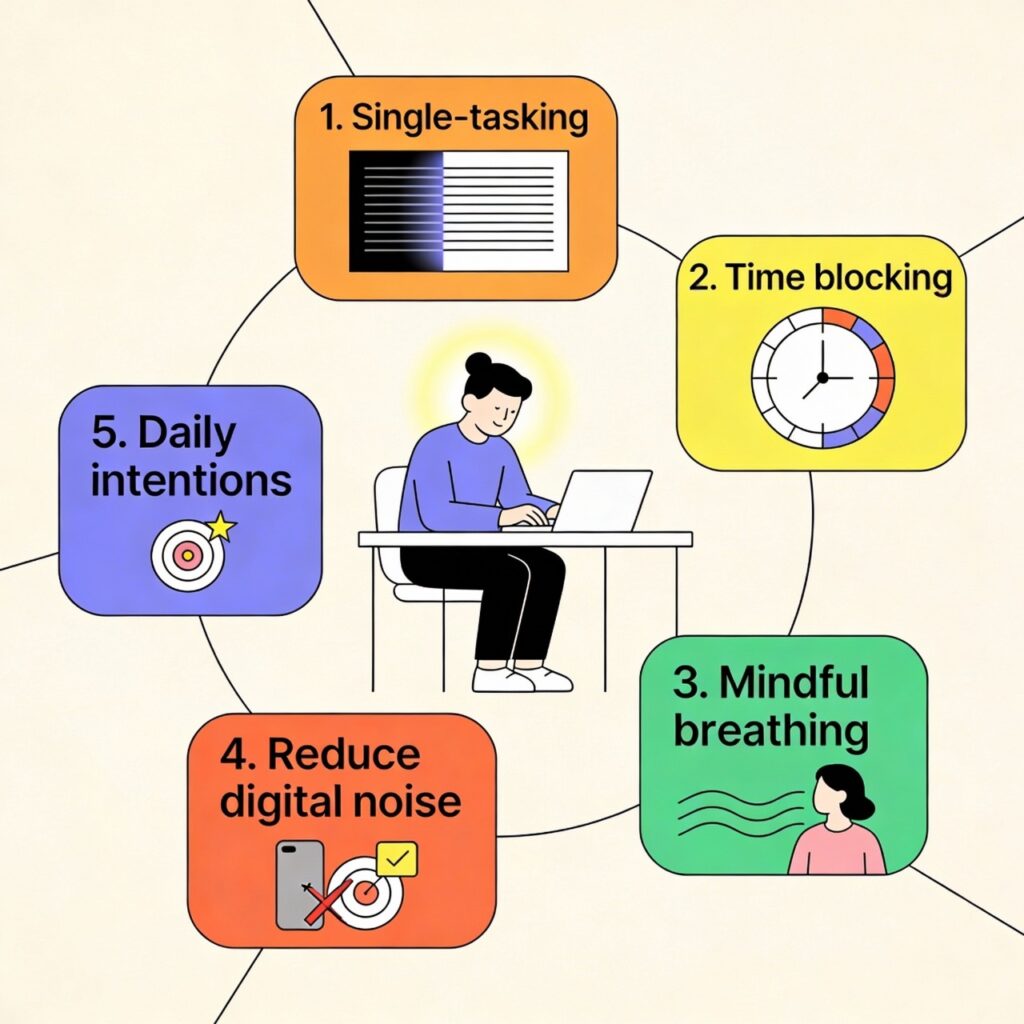
Practice 1: Single-Tasking Instead of Multitasking
Focus improvement starts when the brain is allowed to give full attention to one task at a time. Multitasking may feel efficient, but it forces the mind to jump rapidly between activities. This constant switching increases mental fatigue and reduces the quality of work. Over time, the brain becomes restless and impatient with any task that requires effort.
Focus improvement becomes noticeable when single-tasking is practiced consistently. By staying with one task from start to finish, the mind experiences a sense of completion and calm. This deep engagement improves understanding, memory, and problem solving. The brain also feels less stressed because it is no longer handling competing demands.
Focus improvement strengthens gradually as the brain relearns how to stay present. At first, urges to check the phone or switch tasks may appear frequently. With practice, these urges weaken. Single-tasking trains attention to remain steady, making focus feel natural rather than exhausting.
Practice 2: Time Blocking for Mental Structure
Focus improvement grows when the day is organized into clear time blocks. Without structure, the brain wastes energy deciding what to do next. This constant decision making leads to mental fatigue even before meaningful work begins. Time blocking removes this burden.
Focus improvement increases because the mind feels safer with predictability. When tasks have assigned time slots, attention becomes more purposeful. The brain knows when to work, when to rest, and what to focus on. This clarity reduces anxiety and procrastination.
Focus improvement becomes long lasting as structure turns into routine. The brain starts entering focus mode automatically during work blocks. Over time, attention becomes stronger because the mind is no longer overwhelmed by uncertainty or chaos.
Practice 3: Mindful Breathing to Reset Attention
Focus improvement is supported by mindful breathing because it directly calms the nervous system. When the mind is scattered, breathing slowly sends a signal of safety to the brain. This reduces stress hormones and quiets racing thoughts.
Focus improvement becomes easier because breathing creates a pause between distraction and reaction. Instead of immediately giving in to impulses, the mind learns to slow down. This pause allows attention to return gently to the present task.
Focus improvement deepens with regular breathing practice because awareness increases. The mind becomes better at noticing when focus drifts. With time, breathing becomes a reliable tool to regain clarity during stress or mental overload.
Practice 4: Reducing Digital Distractions
Focus improvement suffers greatly due to constant digital interruptions. Notifications, messages, and app switching condition the brain to expect instant stimulation. This weakens patience and reduces the ability to stay engaged with one task.
Focus improvement increases when digital boundaries are set intentionally. Turning off non essential notifications and creating phone free work periods protect attention. The brain slowly relearns how to stay engaged without constant input.
Focus improvement strengthens over time as the craving for stimulation reduces. The mind becomes comfortable with silence and depth again. Reduced digital noise creates mental space for clarity, creativity, and calm focus.
Practice 5: Setting Clear Daily Intentions
Focus improvement becomes stronger when the mind starts the day with clarity instead of confusion. Without clear intentions, attention reacts to whatever appears first such as messages, demands, or distractions. This reactive mode scatters mental energy and reduces control. Setting clear daily intentions gives the brain a direction .
Focus improvement increases because intentions act like a compass throughout the day. When attention drifts, the mind can gently return to what was chosen as meaningful. This reduces overthinking and prevents unnecessary mental wandering. Intentions also create emotional alignment, helping the brain stay engaged with tasks that actually matter.
Focus improvement becomes consistent as intention setting turns into a habit. Over time, the brain learns to organize attention around purpose instead of urgency. This practice builds mental discipline without pressure and supports deeper concentration, better decision making, and emotional stability.
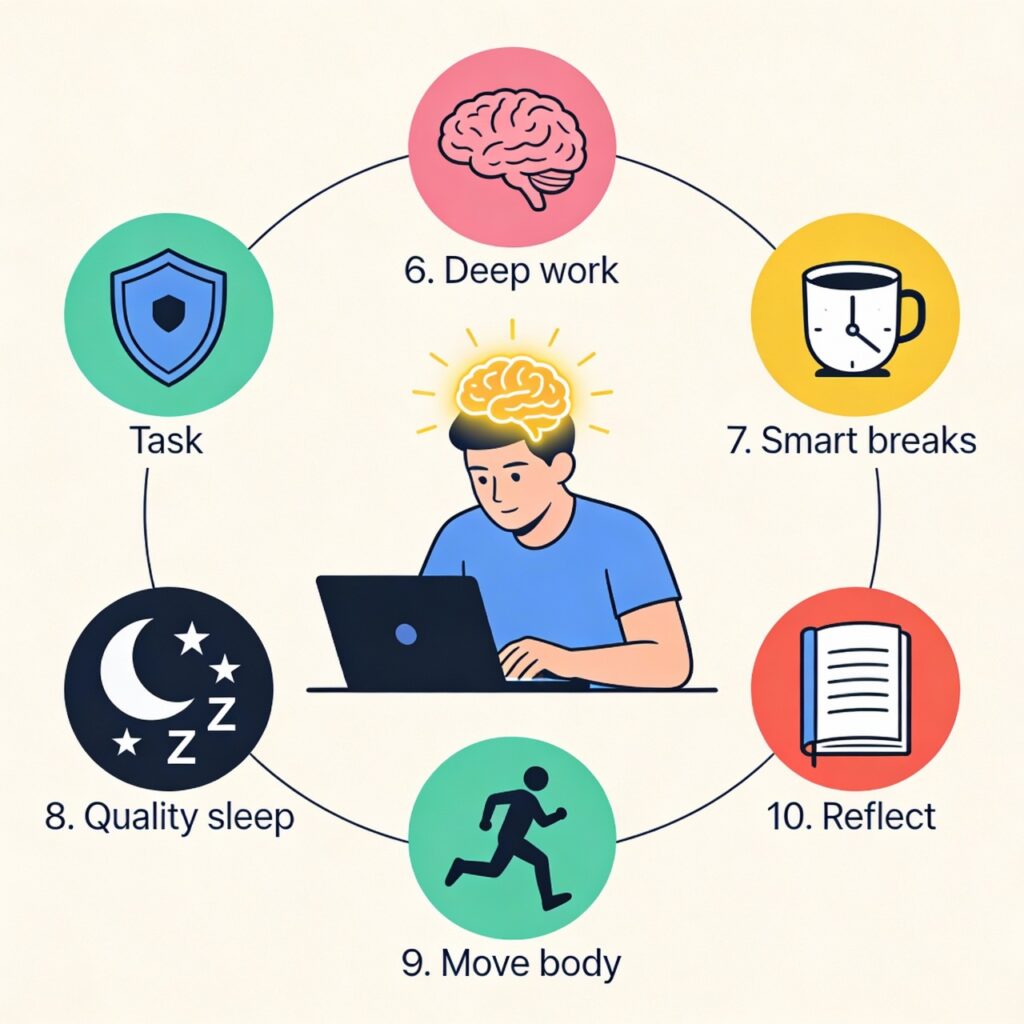
Practice 6: Deep Work Sessions for Cognitive Endurance
Focus improvement grows when the brain practices uninterrupted concentration through deep work sessions. These sessions are designed to protect attention from external noise and internal distractions. Working deeply, even for short periods, teaches the brain that it can stay focused without constant stimulation.
Focus improvement develops endurance because deep work stretches attention slowly and safely. Instead of forcing long hours, gradual exposure builds confidence in sustained focus. Each session strengthens neural pathways responsible for concentration, making the brain more comfortable with mental effort.
Focus improvement becomes reliable as deep work becomes a routine. The brain begins to associate certain times or environments with focus. Over time, entering a deep focus state feels natural, allowing higher quality thinking, creativity, and productivity without exhaustion.
Practice 7: Taking Short, Intentional Breaks
Focus improvement depends on recovery as much as effort. Continuous work without breaks drains attention and increases irritability. Short, intentional breaks allow the brain to process information and release mental tension, preventing burnout.
Focus improvement increases because breaks reset attention instead of weakening it. Stepping away briefly improves clarity and prevents frustration from building up. When breaks are intentional, they refresh the mind rather than distracting it further.
Focus improvement becomes sustainable when rest is respected as part of productivity. Balanced work and rest cycles protect cognitive energy. This practice helps maintain focus throughout the day and supports long term mental health.
Practice 8: Prioritizing Quality Sleep
Focus improvement relies heavily on quality sleep because sleep restores attention control. During rest, the brain repairs neural connections and clears mental fatigue. Without proper sleep, focus weakens no matter how hard one tries.
Focus improvement strengthens with consistent sleep patterns. Going to bed and waking up at regular times stabilizes cognitive rhythm. This improves alertness, memory, and emotional balance during waking hours.
Focus improvement becomes effortless when sleep is treated as a non negotiable priority. A rested brain naturally resists distraction and maintains clarity. Sleep forms the foundation for all other focus habits to work effectively.
Practice 9: Physical Movement to Activate the Brain
Focus improvement increases when the body is active because movement stimulates brain function. Physical activity boosts blood flow, oxygen, and nutrients to the brain, enhancing alertness and attention regulation.
Focus improvement becomes easier as movement releases stress and mental tension. Exercise helps balance mood and reduces restlessness, making it easier to sit and concentrate afterward. Even short walks or stretching sessions can refresh attention.
Focus improvement strengthens when movement becomes part of daily life. Regular activity supports emotional resilience and mental energy. A physically active lifestyle creates the internal conditions needed for sustained focus and clarity.
Practice 10: Daily Reflection for Awareness and Growth
Focus improvement deepens through reflection because awareness reveals how attention is actually used. Reflecting on the day helps identify moments of distraction, clarity, and fatigue. This understanding is essential for growth.
Focus improvement increases because reflection encourages gentle correction rather than self criticism. When patterns are seen clearly, adjustments feel easier and more intentional. The brain learns from experience instead of repeating mistakes.
Focus improvement becomes a lifelong skill when reflection is practiced consistently. Each day becomes feedback for the next. This habit strengthens self control, focus awareness, and long term cognitive growth , making it easier to filter out what is unimportant .
6. How Attention Training Improves Mental Wellness
Focus improvement has a powerful impact on mental wellness because attention decides where the mind spends its energy. When attention is weak, the mind drifts toward worries, regrets, comparisons, and unfinished thoughts. This constant mental wandering creates inner tension and emotional fatigue. Training attention teaches the brain to stay anchored in the present moment, which immediately reduces mental noise and emotional overload.
Focus improvement helps calm the nervous system over time. A distracted mind stays in a reactive state, constantly scanning for threats, updates, or stimulation. This keeps stress hormones active and prevents true relaxation. Attention training gently signals safety to the brain by reducing unnecessary mental movement. As a result, the body relaxes, breathing becomes steadier, and emotional pressure slowly decreases.
Focus improvement reduces anxiety by limiting repetitive thought cycles. Anxiety grows when attention keeps returning to the same fears without resolution. Attention training does not remove thoughts, but it changes the relationship with them. The mind learns to notice thoughts without following them endlessly. This breaks the habit of overthinking and gives the brain space to rest.
Focus improvement strengthens emotional control and maturity. When attention is scattered, emotions quickly take over behavior. Small triggers feel intense, and reactions become impulsive. Trained attention creates a pause between feeling and action. This pause allows awareness, choice, and calmer responses. Over time, emotions feel less overwhelming and easier to manage.
Focus improvement builds confidence through mental stability. When attention stays steady, tasks feel clearer and more manageable. Finishing work without constant distraction builds trust in one’s abilities. This sense of reliability reduces self doubt and mental insecurity. Confidence grows not from motivation, but from repeated focused action.
Focus improvement supports long term emotional resilience. Life stress cannot be avoided, but attention training changes how the mind recovers from stress. Instead of staying stuck in emotional reactions, attention returns to balance faster. This recovery ability strengthens mental toughness and supports lasting mental wellness.
7. Building a Focus-Friendly Environment
Focus improvement depends heavily on the environment because the brain constantly responds to what surrounds it. Even when you are trying to concentrate, the mind continues to scan the space for movement, noise, and visual signals. A busy or disorganized environment keeps the brain alert and distracted, making deep focus feel tiring. Creating a supportive environment reduces this background mental effort and allows attention to settle more easily.
Focus improvement begins with reducing physical clutter. Every object in your field of vision sends a signal to the brain. When there are too many items, the brain processes more information than necessary, which increases mental fatigue. Clearing unnecessary items from desks, rooms, and workspaces helps the brain relax and focus on the task at hand. A simple, clean space gives the mind fewer reasons to wander.
Focus improvement is also influenced by how comfortable the body feels within the space. Poor posture, uncomfortable chairs, or awkward desk height force the brain to constantly adjust and compensate. This physical discomfort quietly steals attention. A supportive chair, proper desk alignment, and relaxed posture allow the mind to stay engaged longer without strain. When the body is at ease, attention becomes more stable.
Focus improvement improves with proper lighting and visual balance. Dim lighting strains the eyes, while harsh lighting increases irritation and fatigue. Natural light or soft, balanced lighting keeps the brain alert without overstimulation. Visual calm, such as neutral colors and minimal decoration, reduces sensory overload and supports longer periods of concentration.
Focus improvement is affected by sound, even when it seems unnoticed. Sudden or irregular noise pulls attention away instantly. Background noise, conversations, or traffic can keep part of the brain in a defensive state. Quiet environments or consistent low-level sounds help attention remain steady. When the brain does not need to react to noise, it can direct energy toward thinking.
Focus improvement also depends on digital surroundings. Open tabs, constant notifications, and switching between apps fragment attention and increase cognitive stress. Each notification trains the brain to expect interruption. Simplifying digital spaces, turning off unnecessary alerts, and limiting open apps protect mental clarity. A calm digital environment is just as important as a clean physical one.
Focus improvement becomes sustainable when the environment supports focus instead of competing with it. When distractions are reduced, focus requires less effort and willpower. The mind naturally enters deeper concentration, mental energy lasts longer, and productivity increases without exhaustion. Over time, a focus-friendly environment trains the brain to associate the space with clarity and deep work.
8. Mistakes That Prevent Focus Improvement
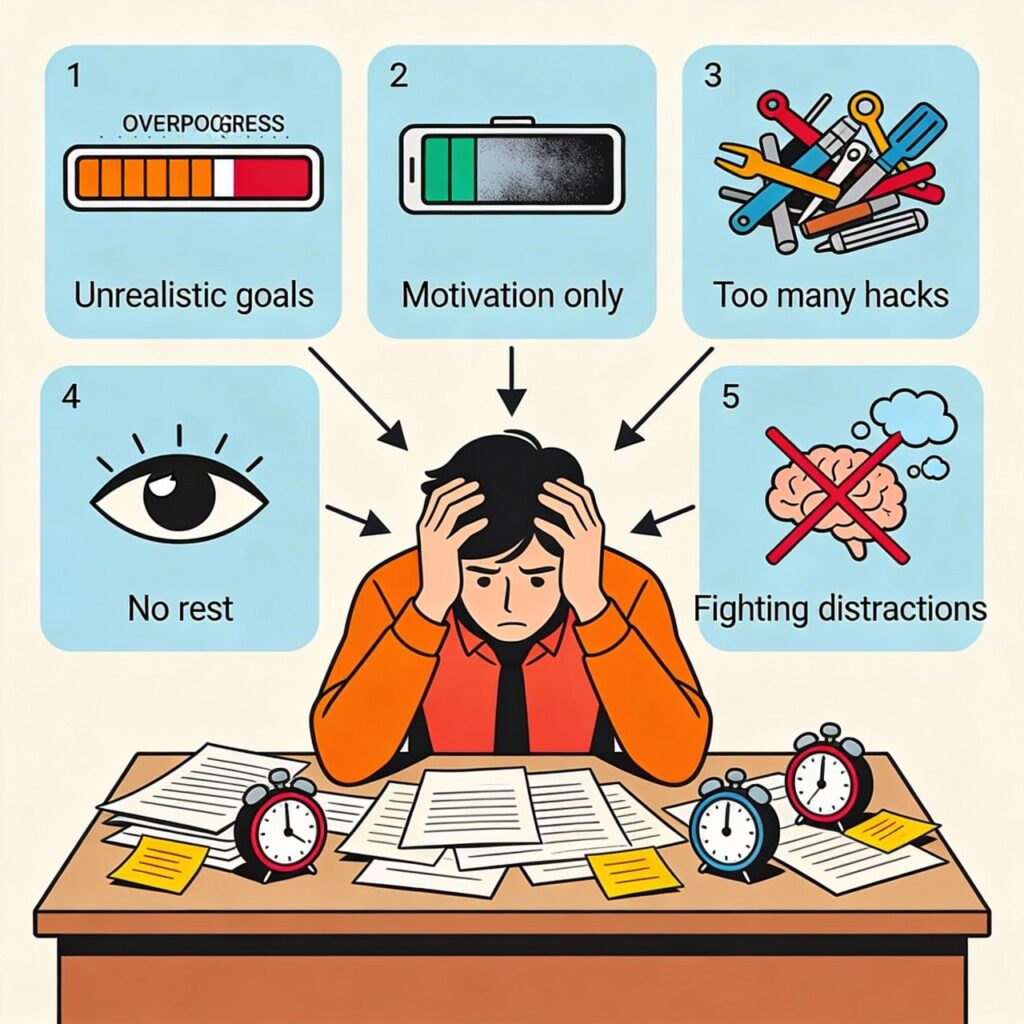
Focus improvement often fails because people set unrealistic expectations about how focus should feel. Many believe they should be able to concentrate for long hours without effort or distraction. When this does not happen, frustration builds and people give up quickly. In reality, focus grows gradually. Expecting instant deep focus puts pressure on the mind and creates resistance instead of progress.
Focus improvement also suffers when people try to rely only on motivation. Motivation comes and goes based on mood, energy, and circumstances. When focus depends on motivation alone, consistency breaks easily. On low motivation days, attention collapses. Routine and structure are far more reliable than emotional drive. Habits protect focus even when motivation is low.
Focus improvement is weakened by trying too many techniques at once. Switching between methods creates confusion and overload. The brain needs repetition and simplicity to learn new patterns. When too many tools are used together, attention scatters instead of strengthening. Choosing a few simple practices and repeating them daily allows focus to grow steadily.
Focus improvement fails when rest and recovery are ignored. Many people believe resting means losing time, but the opposite is true. Without proper breaks, the brain becomes fatigued and attention quality drops sharply. Overworking trains the brain to associate focus with exhaustion. Balanced work and rest help attention remain sharp and sustainable.
Focus improvement becomes difficult when distractions are fought aggressively instead of managed gently. Forcing the mind to suppress thoughts increases mental tension. Attention improves when distractions are noticed calmly and redirected without judgment. Avoiding these common mistakes allows focus to develop naturally, steadily, and without burnout.
9. Turning Focus Improvement into a Daily Lifestyle
Focus improvement becomes truly effective when it is treated as a lifestyle choice rather than a temporary productivity experiment. Many people try to focus only when deadlines approach, but this creates pressure and inconsistency. When focus habits are practiced daily, even on calm or low pressure days, the brain learns stability. This steady practice builds a strong foundation for long term attention and mental clarity.
Focus improvement grows when daily routines are designed to support the brain instead of fighting it. Fixed wake up times, regular meals, planned work periods, and intentional rest create a predictable rhythm. This rhythm reduces mental friction and helps the brain transition smoothly between focus and recovery. When the mind knows what to expect, it resists distractions less and concentrates more naturally.
Focus improvement also depends on how attention is treated emotionally. When focus is forced with self criticism, the mind becomes tense and resistant. When attention is guided with patience and curiosity, the brain feels safe to settle. A focus friendly lifestyle encourages gentleness rather than pressure. This emotional approach makes attention stronger and more cooperative over time.
Focus improvement becomes sustainable when awareness is practiced throughout the day. Noticing when attention drifts, understanding why it happened, and calmly bringing it back builds self regulation. This awareness prevents unconscious habits from taking over. Small moments of correction repeated daily slowly reshape how the brain uses attention.
Focus improvement requires patience because mental change happens gradually. Progress may feel slow at first, but consistency compounds results. Each focused moment trains the brain slightly more. Over weeks and months, these small changes add up to noticeable clarity, better decision making, and reduced mental noise.
Focus improvement eventually becomes part of personal identity. Instead of saying you are trying to focus, you begin to live in a focused way. Tasks feel more intentional, conversations feel deeper, and the mind feels calmer. A focused lifestyle brings mental peace, confidence, and a stronger sense of control over time and energy.
10. Conclusion
Focus improvement is not about forcing the mind or relying solely on willpower. It is about creating an environment and lifestyle that naturally support sustained attention. By developing consistent daily habits, reducing distractions, and practicing gentle attention exercises, anyone can gradually strengthen focus. Over time, these small and repeated actions rewire the brain to maintain concentration more easily, even in a distraction-heavy world. The process requires patience, awareness, and deliberate effort, but the results are lasting and transformative.
Focus improvement directly enhances mental wellness. When attention becomes stable, the mind experiences less stress, anxiety, and mental clutter. Tasks are completed more efficiently, decisions are clearer, and emotional reactivity is reduced. A calm, focused mind allows better problem-solving, creativity, and rational thinking. This improved mental clarity has a ripple effect on every aspect of life, from professional performance to personal relationships, creating a sense of inner balance and control.
Focus improvement strengthens self-discipline and emotional resilience. Regular practice trains the mind to resist impulsive distractions and remain engaged with meaningful tasks. Emotional ups and downs are easier to manage because the mind learns to observe thoughts and feelings without immediately reacting. This self-regulation builds confidence and reduces frustration, making challenges feel manageable rather than overwhelming. The consistent practice of focus becomes a foundation for long-term psychological stability and personal growth.
Focus improvement is most effective when it is integrated into lifestyle choices. Structured routines, proper sleep, regular physical activity, mindfulness practices, and reduced digital overstimulation all support attention naturally. When focus habits are reinforced through daily rituals, they become automatic, reducing the mental effort needed to concentrate. The brain adapts to this supportive environment, gradually making deep focus a default state rather than an occasional effort.
Focus improvement is ultimately a journey toward a more intentional, balanced, and meaningful life. At Mindquora, attention is seen as a tool for mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall well-being. By practicing focus improvement consistently, individuals gain not just productivity, but a stronger sense of purpose, calmer mind, and improved quality of life. With awareness, patience, and dedicated practice, focus becomes a powerful ally rather than a source of struggle, transforming everyday experiences into moments of presence, clarity, and fulfillment.
